The TextBox Control
- Details
- Written by David Corrales
- Last Updated: 13 June 2016
- Created: 13 June 2011
- Hits: 101575
TextBox [System.Windows.Forms.TextBox]
Creates a text box for displaying text and collecting user input in text format.
- MSDN Page: System.Windows.Forms.TextBox
- Default Event: TextChanged
Tip: Because many of the properties of Textbox objects are inherited from the TextBoxBase class, these properties are available on other controls that are derived from TextBoxBase, including MaskedTextBox and RichTextBox.
Need to scroll to the end of a textbox? Try this Textbox tip!
Important Properties
| • Text | Get, set, change the text in a textbox |
| • Font | Determine the style and size of the textbox text |
| • Multiline | Resize and allow multiple lines of text |
| • ReadOnly | Determines whether the user can change Textbox text |
| • MaxLength | Maximum characters a user can enter |
| • WordWrap | Enables/disables word wrap |
| • ScrollBars | Determines which scroll bars are enabled |
| • UseSystemPasswordChar | Displays a character instead of typed text |
| • AutoCompleteMode | Determines the text completion behavior |
| • AutoCompleteSource | Specifies the data source for the auto-complete strings |
| • AutoCompleteCustomSource | Specifies auto-complete values |
Important Methods
| • AppendText | Appends text to the text in the text box |
Important Events
| • TextChanged | event: Occurs when the value of the Text property changes |
Important Properties
Text property: Manages the text in the textbox
Use the Text property to get, set, and change the text in the textbox.
- MSDN page: Text
- Value type: System.String
- Default value: (None)
Get the text in a textbox. This can be text that a user typed in the textbox or text that your script added to the textbox.
$text = $textbox1.Text |
Set the text in a textbox. This command makes text appear in the textbox.
$textbox1.Text = "Display this text" |
Display cmdlet output in a textbox. Be sure to format the content into string output.
$textboxProcess.Text = Get-Process | Format-Table | Out-String |
Font property: Determines the style and size of the text in the textbox
Use the Font property to get, set, or change the font of text in the Textbox.
- MSDN page: Font
- Value Type: System.Drawing.Font
- Default: Microsoft Sans Serif 8.25
To display Windows PowerShell output correctly aligned, use a monospace font, such as Courier New, Consolas, or Lucida Console.
Output in Microsoft Sans Serif:
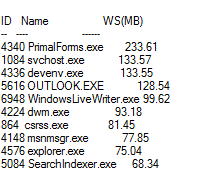
Same output in Lucida Console:
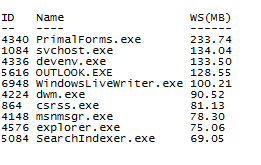
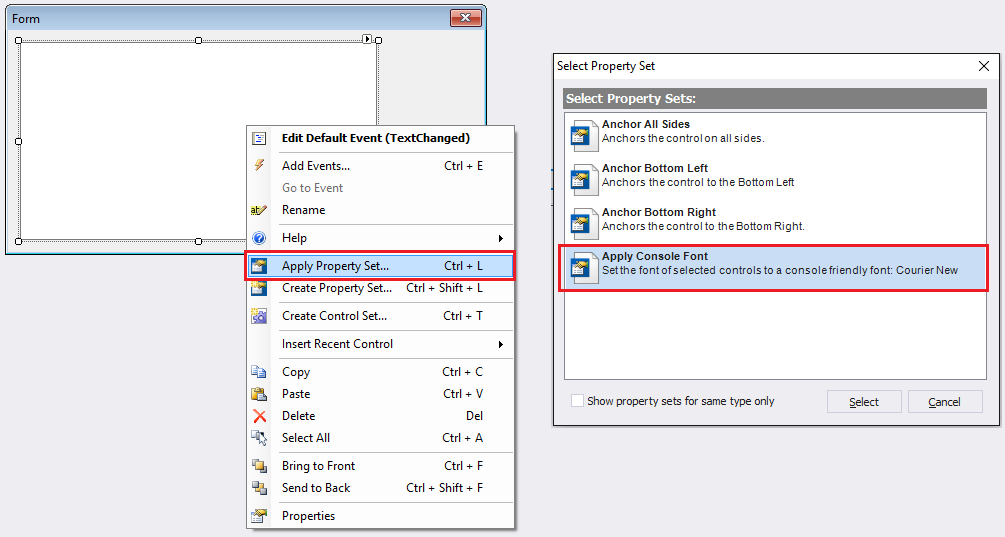
Tip: To set the font to display Windows PowerShell output, right-click the textbox, click Apply Property Set, and then click Apply Console Font.
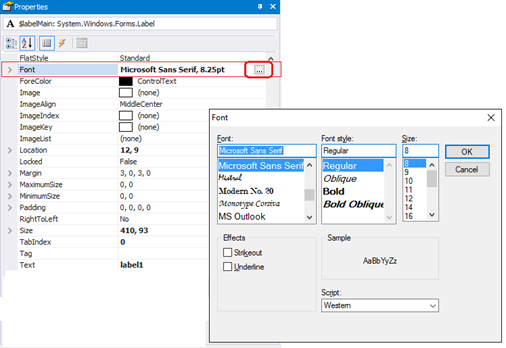
To set the font easily, in the Properties pane for the Label, in the Font row, click the ellipsis (…) and then use the Font selector.
To display the properties of the Font object, in the Properties pane, click the Font group arrow.
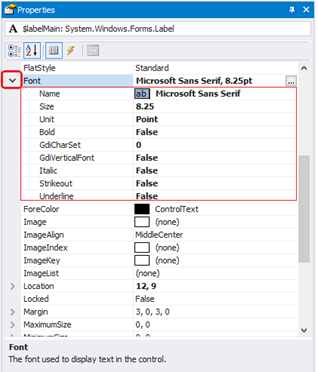
To script a font change, set the Font property to a string with the Font name, size, and style.
$labelMain.Font = 'Segoe UI, 15.75pt, style=Bold, Italic' |

To determine other properties of the font, create a System.Drawing.Font object.
$ClickFont = [System.Drawing.Font]::new('Microsoft Sans Serif', 8.25, [System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Regular) $ClickedFont = [System.Drawing.Font]::new('Segoe UI', 16, [System.Drawing.FontStyle]::Italic) $labelMain_Click={ if ($labelMain.Text -eq 'Click') { $labelMain.Text = 'Clicked' $labelMain.Font = $ClickedFont } else { $labelMain.Text = 'Click' $labelMain.Font = $ClickFont } } |
Tips:
- To enlarge the label automatically to fit its contents, set the AutoSize property of the Label to $True.
- When scripting a font, be sure to set the Font property of the Label. The Text property of the Label does not have a Font property.
Multiline property: Resize and permit multiple lines of text
Use the Multiline property to resize a textbox or allow you or the user to type multiple lines of text in the textbox. By default, the textbox is single line.
- MSDN page: Multiline
- Value type: System.Boolean (True, False)
- Default value: False
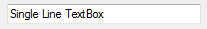
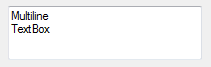
For example, the following images show a single-line (Multiline=$False) and multi-line (Multiline = $True) textbox.
Single Line TextBox:
Multi-Line TextBox:
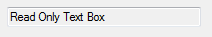
ReadOnly property: Determines whether the user can change Textbox text
Use the ReadOnly property when you want to display text and prevent the user from changing the contents.
- MSDN page: ReadOnly
- Value type: System.Boolean (True, False)
- Default value: False
Important: When the ReadOnly property is True, the TextBox background is grey, the text is black, and changes to the ForeColor (text color) property have no effect. To change the color of the Textbox background and make changes to the ForeColor property effective, use a RichTextBox or change the BackColor property.
MaxLength property: Maximum characters a user can enter
Use MaxLength property to specify the maximum number of characters that an end-user can enter into the textbox, such as when a user name or password has a length limit. The MaxLength property value does not limit that the text that you (as the designer) or your script can enter in the textbox.
- MSDN page: MaxLength
- Value type: System.Int32
- Default value: 32767
WordWrap property: Enables/disables word wrap
When WordWrap is $True, lines of text that exceed the length of a multiline textbox are restarted on the next line. Set the value of WordWrap to $False when you do not want to alter the formatting of the text, such as text in Windows PowerShell output.
- MSDN page: WordWrap
- Value type: System.Boolean (True, False)
- Default value: True
WordWrap has no effect on single-line textboxes, but it is equally effective on text that the end-user types and text that the scripts assigns to the textbox. When word-wrapping isn’t useful, consider resizing the textbox to fit the text.
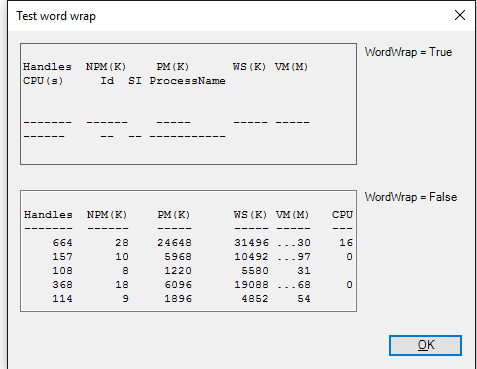
ScrollBars property: Determines which scroll bars are enabled
Use the ScrollBars property to enable and disable horizontal and vertical scroll bars on multiline textboxes.
- MSDN page: ScrollBars
- Value type: System.Windows.Forms.Scrollbars enumeration
- Default value: None
Valid values:
None
No scroll bars are shown.
Horizontal
Only horizontal scroll bars are shown.
Vertical
Only vertical scroll bars are shown.
Both
Both horizontal and vertical scroll bars are shown.
NOTE: Scroll bars are active only when the text exceeds the horizontal or vertical dimension of the textbox.
UseSystemPasswordChar property: Displays a character instead of typed text
Use the UseSystemPasswordChar property to mask characters that are typed into the textbox. Instead of the typed character, a character selected by the operating system, typically *, appears. To set the character, use the PasswordChar property. When both are set, UseSystemPasswordChar takes precedence.
- MSDN page: UseSystemPasswordChar
- Value type: System.Boolean (True, False)
- Default value: False

Auto Complete Properties:
Use the following properties to manage the built-in auto-complete features of a TextBox.
AutoCompleteMode property: Determines the text completion behavior
Use the AutoCompleteMode property to select how the auto-completion occurs.
- MSDN page: AutoCompleteMode
- Value type: System.Windows.Forms.AutoCompleteMode
- Default value: None
Valid values :
- Append
- Appends the remainder of the most likely candidate string to the existing characters, highlighting the appended characters.
- Suggest
- Displays the auxiliary drop-down list associated with the edit control. This drop-down is populated with one or more suggested completion strings.
SuggestAppend- Appends both Suggest and Append options.
None (Default)- Disables automatic completion.
AutoCompleteSource property: Specifies the data source for auto-completing
Use the AutoCompleteSource property to specify the source of the data used to complete text in a textbox. You can use a custom list of words or select a built in source, such as the file system.
- MSDN page: AutoCompleteSource
- Value type: System.Windows.Forms.AutoCompleteSource enumeration
- Default value: None
Valid values:
FileSystem
Uses the file system as the source. The field auto-completes file and folder names.
HistoryList
Auto-completes Uniform Resource Locators (URLs) in the history list.
RecentlyUsedList
Auto-completes recently used Uniform Resource Locators (URLs).
AllUrl
Combines HistoryList and RecentlyUsedList contents.
AllSystemSources
Combines FileSystem and AllUrl sources. This is the default value when AutoCompleteMode is set to a value other than Default.
FileSystemDirectories
Auto-completes only file system directory names, not file names.
CustomSource
Auto-completes the strings specified by the AutoCompleteCustomSource property.
None (Default)
Does not specify an auto-complete source. This is the default value of AutoCompleteSource.
ListItems
Applies only to the ComboBox control. Specifies that the items of the ComboBox represent the source.
AutoCompleteCustomSource property: Specifies auto-complete values
Use the AutoCompleteCustomSource property to define your own list of auto-complete strings. This list is used when the value of the AutoCompleteSource property value is CustomSource.
- MSDN page: AutoCompleteCustomSource
- Value type: System.Windows.Forms.AutoCompleteStringCollection
- Default value: None
In this example, the auto-complete source is a list of computer names in the Computers.txt file. The AddRange method adds a collection of items.
$computers = Get-Content C:\computers.txt" $textbox1.AutoCompleteCustomSource.AddRange($computers) |
Important Methods
AppendText method: Appends text to the text in the text box
Use the AppendText method to add strings to the value of the Text property of a text box. It is more efficient than using the += operator.
Note: The AppendText method is defined in the TextBoxBase class and is inherited by its child classes, Textbox, MaskedTextBox, and RichTextBox, and their child classes, such as DataGridTextBox.
- MSDN page: AppendText
- Value type: System.String
- Default value: None
In this example, we use the AppendText method of the Textbox to add a year to a list of years in the textbox.
$textboxOutput.Text = "2012, 2014, 2015" if (Test-Path "$env:ProgramFiles\*\PowerShell Studio 2016") { $textboxOutput.AppendText(", 2016`r`n") } |
Important Events
TextChanged event: Occurs when the value of the Text property changes
Use the TextChanged event to respond to a user entering, deleting, or changing the Text in a Textbox.
- MSDN page: TextChanged
- Default value: None
For example, this event handler enables the $buttonSubmit button when the text in the $textboxUser textbox is not an empty string.
$textboxUser_TextChanged = { $buttonSubmit.Enabled = $textboxUser.Text -ne '' } |
How to scroll to the end of a TextBox:
This tip explains how to position the cursor at the end of the $textbox1 textbox, that is, to the right of text typed in the box.
$textbox1.SelectionStart = $textbox1.Text.Length $textbox1.ScrollToCaret() |
The first command uses the SelectionStart property of the Textbox to set the starting point of the text at the position of the last character of text in the $textbox1 Textbox. The second command uses the ScrollToCarat method to place the cursor at the SelectionStart value location.
For licensed customers, use the forum associated with your product in our Product Support Forums for Registered Customers.
For users of trial versions, please post in our Former and Future Customers - Questions forum.


